MODIFIED ON: November 29, 2022 / ALIGNMINDS TECHNOLOGIES / 0 COMMENTS

In 1985, Canada’s Therac-25 radiation therapy machine malfunctioned due to software bug and delivered lethal radiation doses to patients, leaving 3 people dead and critically injuring 3 others.
During the first Gulf War, an American Patriot Missile system in Saudi Arabia failed to intercept an incoming Iraqi Scud missile due to a software rounding error in calculation. The missile destroyed an American Army barracks and 28 soldiers dead, 100 injured.
In May of 1996, a software bug caused the bank accounts of 823 customers of a major U.S. bank to be credited with 920 million US dollars.
Do you realize, how Testing is vital?
Do you think, understanding a product and testing the same against functionality, performance, security, GUI and many others is an easy task?
We can implement new & better choices for a product’s quality and security. There are lots of ways to test our product.
The most accepted deal is unit testing. Also, we should need to write functional or acceptance tests as well. For all these Codeception is the right choice! The Codeception testing framework figures out all these levels of testing and it is a multi-featured testing framework for PHP.
Codeception can handle unit, functional, and acceptance testing of web applications.

Major types of Tests
It was evoked in November 2011 and released the first stable version 1.0 in January 2012. Codeception tries to simplify and combine the process of writing tests, plugging different testing suites with the use of modules and it opens the way to anyone to extend and sharpen it. Codeception is testing framework in which all tests are written in a single descriptive manner.
What variety of tests & How?
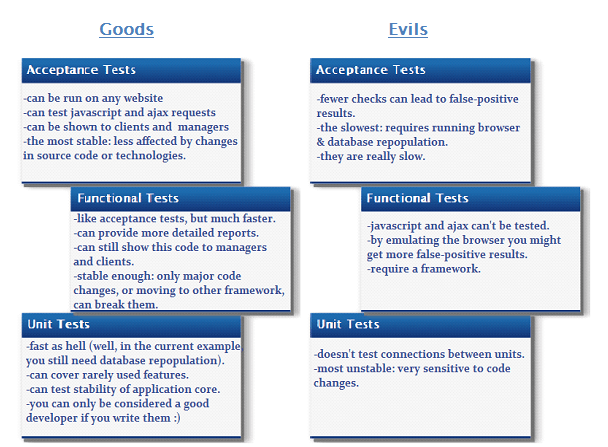
Major types of Tests covered and its Pros & Cons
Acceptance Test (WebGuy)
Acceptance testing can be performed by a non-technical person. That person can be your tester, manager or even client. It allows us to test our applications using the normal website viewing process i.e.; visit a webpage, fill in a form, and submit the form to see the desired result.
The difference is with Codeception, we don’t have to waste time going to the browser each time we want to test a new feature out, instead, we can just run our acceptance tests to see its passes or not.
Try a sample scenario;
Probably the first test you would want to run would be signing in. In order to write such a test, we still require basic knowledge of PHP and HTML.
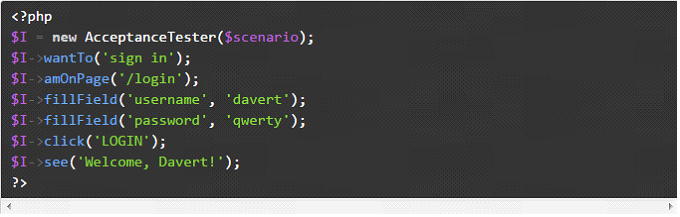
This scenario can probably be read by non-technical people. Codeception can even ‘naturalize’ this scenario, converting it into plain English:

It can be done by command:

The Want To section describes your scenario in brief. The $I object is used to write all interactions. The methods of the $I object are taken from the PhpBrowser and Db modules. We assume that all am commands should describe the starting environment. The amOnPage command sets the starting point of a test to the /login page. With the PhpBrowser you can click the links and fill the forms. That will probably be the majority of your actions.
Functional Test (TestGuy)
We can check our application without running it on a server, this is what done on Functional tests. These tests are written in the same way as Acceptance tests with PhpBrowser module enabled. It’s tested by a technically advanced guy i.e., TestGuy. The TestGuy knows how the application works, passes different $_GET, $_POST and $_REQUEST variables to assure the functionality. Codeception can connect to numerous web frameworks Symfony2, Laravel4, Yii2, Zend Framework and others which support functional testing.
We can open a web page with amOnPage command.
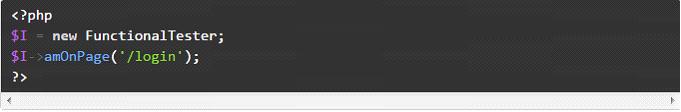
We can click links to open web pages of the application.

Functional tests will perform much better if we use powerful frameworks. It allows us to access and manipulate their internal states and this helps our tests shorter and faster. On the other hand, if we do not use frameworks there is no practical reason to write functional tests.
Let’s allow our application tested by this technically advanced guy for better results.
Unit Test (CodeGuy)
“Unit” casually refers to low-level tests and the developer understands how and what is tested here, though some would say a better name is DeveloperTest. The person testing, CodeGuy, knows the internals of the application and tests database operations and anything else that might need proof of concept. Codeception provides some well-built tools to make your unit tests simpler and cleaner. Even inexperienced developers should understand what is tested and how.
We can start with generating a classical PHPUnit test by this command:

We can use another command to create Codeception-powered unit tests.

Both tests will create a new ExampleTest file located in tests/unit directory.
A test created by generate:test command will look like this:
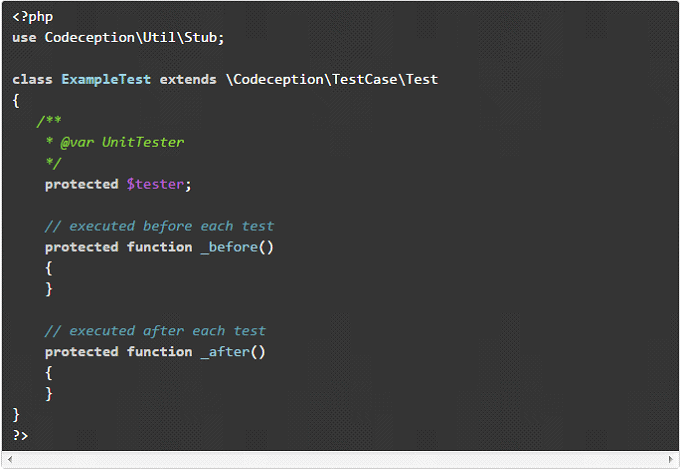
This class has predefined _before and _after methods to start with. We can use them to create a tested object before each test and destroy it afterwards. All Codeception tests are written in a descriptive manner. We can easily catch it from the test body. Its aim is to make tests easy to read, easy to write and easy to debug.
After all, this is how the Codeception works and you should give it a try on yourself.
Go ahead, use Codeception skillfully.
(Reference: codeception.com)
Leave a reply
Your email address will not be published.
-
Recent Posts
- The Role of AI in Business Growth: Top Trends for 2025 and Beyond
- The Evolution of Voice Search in AI: What’s Next for 2025?
- How to Hire an AI Developer: A Complete Guide 2025
- Top 10 Android App Development Trends in 2025
- Top Trends in Product Modernization for 2025 and Beyond
-
Categories
- MVP Development (5)
- AlignMinds (56)
- Operating Systems (1)
- Android POS (3)
- Application Hosting (1)
- Artificial Intelligence (49)
- Big Data (2)
- Blockchain (1)
- Cloud Application Development (8)
- Software Development (39)
- Software Testing (9)
- Strategy & User Experience Design (4)
- Web Application Development (28)
- Cyber Security (6)
- Outsourcing (7)
- Programming Languages (3)
- DevOps (5)
- Software Designing (6)
- How to Code (4)
- Internet of Things (1)
- Machine Learning (2)
- Mobile App Marketing (5)
- Mobile Application Development (25)
- Mobile Applications (11)







