MODIFIED ON: November 29, 2022 / ALIGNMINDS TECHNOLOGIES / 0 COMMENTS

Smartphones are widely used across the world today, hence the security threats are also widely spread. Our phones have become the most connected devices, at the same time the least secure. The security threats we face are those which we fail to notice and will be more hazardous in the near future. Let us look at some of the major security threats that every mobile user must be aware of.
Cryptojacking
Cryptojacking is defined as the secret use of your smartphone device by the attacker to mine cryptocurrency.
Cryptojacking used to be confined to the victim unknowingly installing a program that secretly mines cryptocurrency.
When using browser there is no need of a separate program to do the In-browser crypto-jacking.
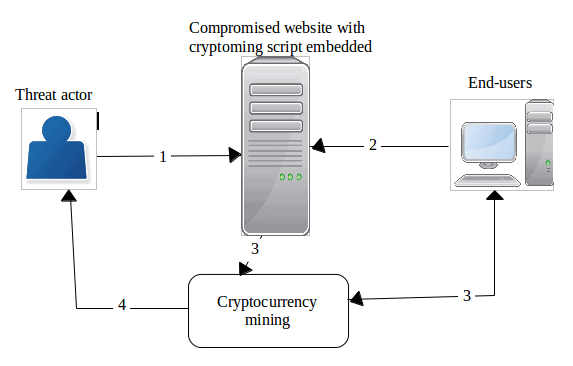
- The threat actor compromises a website
- The crypto mining script executes when the user connects to the compromised website.
- Users unknowingly start mining cryptocurrency on behalf of the threat actor
- When successfully adding a new block to the blockchain, the threat actor receives a reward in cryptocurrency coins.
Insecure communications
The networks that you use to communicate are never fully foolproof, making your device vulnerable to attacks from malware. There are chances that hackers tend to set-up fake access points when you access Wi-Fi in public places such as coffee shops, airports, etc. The access points are named using nonexclusive names, which can fool even the most brilliant people.
It is always good to be cautious when connecting to public Wi-Fi. Use public Wi-Fi only if extremely required and never use it to access personal information like bank account access etc.
Mobile ransomware
A form of ransomware which affects only mobile devices is called mobile ransomware.
A cybercriminal uses mobile malware to steal sensitive data from smartphones or attempts to lock a device, before demanding payment to return the data to the user or to unlock the blocked device. Sometimes people may find some innocent content or some software through social networks, which they download accidentally and get tricked into downloading some malicious ransomware.
After the malware is downloaded onto a device, it will ask the user to pay an amount before encrypting files and locking the phone. After the payment is processed online, often via Bitcoin, the ransomware will send a code to unlock the phone or data.
While installing any app, make sure the app is downloaded from Google Play or App Store than from any third-party app stores.
Phishing attacks
A social engineering attack often used to steal user data, including login credentials and credit card numbers is called Phishing.
It occurs when an attacker fools the victim into opening an email, instant message, or text message by acting as a trusted entity.
User can play smart by not clicking any unfamiliar email links. Always enter URLs manually as much as possible.
SMS–based attacks
From the email world, the phishing has evolved into the SMS world. You get SMS texts and links that you are asked to open to authenticate certain information. To any novice user, the links and the sender would seem genuine. However, clicking on these links can make your device vulnerable to the attacks, and in turn, give away your confidential information. This is a developing security threat for your mobile device.
Botnets attack
A botnet is just a short form for the terms “robot” and “network”.
A botnet is a number of web-connected devices, each of which is running one or more bots. Botnets can be used to perform distributed refusing of service attack (DDoS attack), send spam, steal data, and allows the attacker to access the device and its connection.
A botnet attack firstly requires creating numerous botnets or a botnet army. Once the attack is initiated, these botnets are used to send network/Internet-based requests to the target system in a large quantity. These requests can be in the form of bulk email messages to simple ping messages. The attack can slow down the network/server, making it busy or unable for others to access it or temporarily freeze the server.
Distributed denial of service (DDOS) is a common example of a botnet attack that utilizes a number of botnet devices to send a large number of simultaneous requests/packets to the targeted system.
Installing effective antivirus/anti-malware software can protect your device from such attacks.
User & device authentication
Most mailing apps have provided the user & device authentication, which has allowed the user to store passwords, and their data on the devices. If the device is stolen, your authentication and the data will be at risk. This is one of the major threats to mobile devices, as they contain our valuable personal pieces of information.
The smartphone is a device that blurs the boundaries between professional and personal life and the users are up to three times more likely to be the victims of mobile threats. Safe browsing, identifying suspicious files or phishing emails, ensuring safe data access at public Wi-Fi networks, safe downloads are some of the important tips that a user must be careful about. Other than these security measures, several mobile security software is available to download from Google Play and App Store to ensure safety in your mobile devices.
Understanding these common security threats and implementing recommended solutions can help you protect data in your smartphone.
Leave a reply
Your email address will not be published.
-
Recent Posts
- The Role of AI in Business Growth: Top Trends for 2025 and Beyond
- The Evolution of Voice Search in AI: What’s Next for 2025?
- How to Hire an AI Developer: A Complete Guide 2025
- Top 10 Android App Development Trends in 2025
- Top Trends in Product Modernization for 2025 and Beyond
-
Categories
- MVP Development (5)
- AlignMinds (56)
- Operating Systems (1)
- Android POS (3)
- Application Hosting (1)
- Artificial Intelligence (49)
- Big Data (2)
- Blockchain (1)
- Cloud Application Development (8)
- Software Development (39)
- Software Testing (9)
- Strategy & User Experience Design (4)
- Web Application Development (28)
- Cyber Security (6)
- Outsourcing (7)
- Programming Languages (3)
- DevOps (5)
- Software Designing (6)
- How to Code (4)
- Internet of Things (1)
- Machine Learning (2)
- Mobile App Marketing (5)
- Mobile Application Development (25)
- Mobile Applications (11)







